来源:www.liaoxuefeng.com
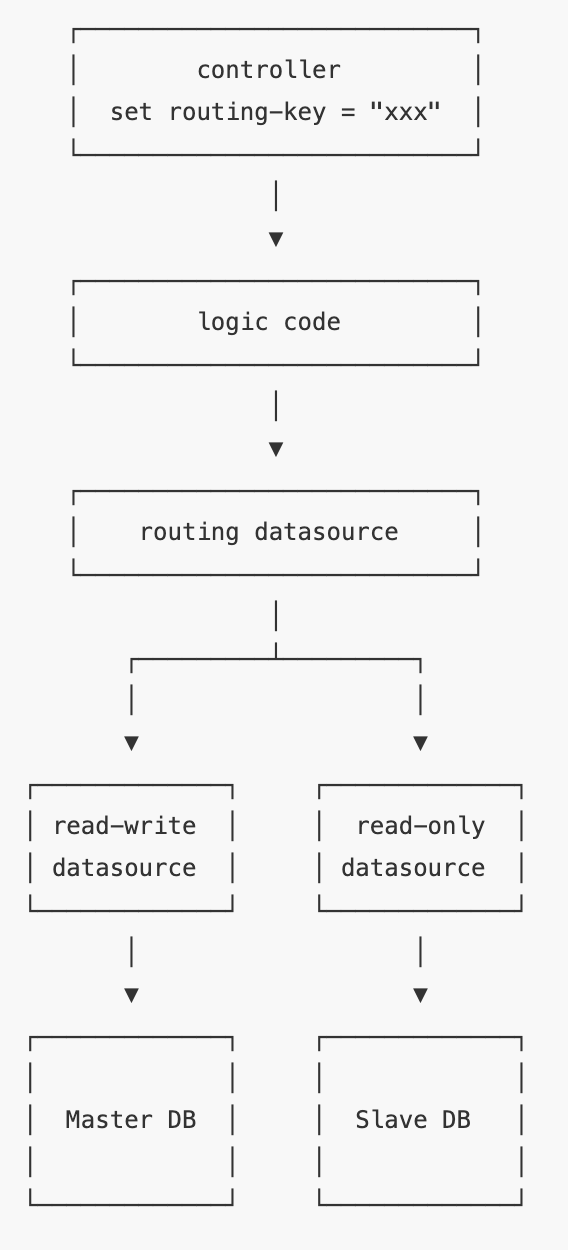
第一步:配置多资料源
Spring Boot 基础就不介绍了,推荐下这个实战教程:
https://github.com/javastacks/spring-boot-best-practice
首先,我们在 SpringBoot 中配置两个资料源,其中第二个资料源是ro-datasource:
spring:
datasource:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost/test
username: rw
password: rw_password
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
hikari:
pool-name: HikariCP
auto-commit: false
...
ro-datasource:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost/test
username: ro
password: ro_password
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
hikari:
pool-name: HikariCP
auto-commit: false
...
在开发环境下,没有必要配置主从数据库,只需要给数据库设定两个用户,一个rw具有读写权限,一个ro只有 SELECT 权限,这样就模拟了生产环境下对主从数据库的读写分离,
在 SpringBoot 的配置代码中,我们初始化两个资料源:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MySpringBootApplication {
/**
* Master data source.
*/
@Bean("masterDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
DataSource masterDataSource() {
logger.info("create master datasource...");
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* Slave (read only) data source.
*/
@Bean("slaveDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.ro-datasource")
DataSource slaveDataSource() {
logger.info("create slave datasource...");
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
...
}
第二步:撰写 RoutingDataSource
然后,我们用 Spring 内置的 RoutingDataSource,把两个真实的资料源代理为一个动态资料源:
public class RoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return "masterDataSource";
}
}
对这个RoutingDataSource,需要在 SpringBoot 中配置好并设定为主资料源:
@SpringBootApplication
public class MySpringBootApplication {
@Bean
@Primary
DataSource primaryDataSource(
@Autowired @Qualifier("masterDataSource") DataSource masterDataSource,
@Autowired @Qualifier("slaveDataSource") DataSource slaveDataSource
) {
logger.info("create routing datasource...");
Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("masterDataSource", masterDataSource);
map.put("slaveDataSource", slaveDataSource);
RoutingDataSource routing = new RoutingDataSource();
routing.setTargetDataSources(map);
routing.setDefaultTargetDataSource(masterDataSource);
return routing;
}
...
}
现在,RoutingDataSource 配置好了,但是,路由的选择是写死的,即永远回传"masterDataSource",
现在问题来了:如何存盘动态选择的 key 以及在哪设定 key?
在 Servlet 的执行绪模型中,使用 ThreadLocal 存盘 key 最合适,因此,我们撰写一个 RoutingDataSourceContext,来设定并动态存盘 key:
public class RoutingDataSourceContext implements AutoCloseable {
// holds data source key in thread local:
static final ThreadLocal<String> threadLocalDataSourceKey = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static String getDataSourceRoutingKey() {
String key = threadLocalDataSourceKey.get();
return key == null ? "masterDataSource" : key;
}
public RoutingDataSourceContext(String key) {
threadLocalDataSourceKey.set(key);
}
public void close() {
threadLocalDataSourceKey.remove();
}
}
然后,修改 RoutingDataSource,获取 key 的代码如下:
public class RoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return RoutingDataSourceContext.getDataSourceRoutingKey();
}
}
这样,在某个地方,例如一个 Controller 的方法内部,就可以动态设定 DataSource 的 Key:
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Get("/")
public String index() {
String key = "slaveDataSource";
try (RoutingDataSourceContext ctx = new RoutingDataSourceContext(key)) {
// TODO:
return "html... www.liaoxuefeng.com";
}
}
}
到此为止,我们已经成功实作了数据库的动态路由访问,
这个方法是可行的,但是,需要读从数据库的地方,就需要加上一大段try (RoutingDataSourceContext ctx = ...) {}代码,使用起来十分不便,有没有方法可以简化呢?
有!
我们仔细想想,Spring 提供的宣告式事务管理,就只需要一个@Transactional()注解,放在某个 Java 方法上,这个方法就自动具有了事务,
我们也可以撰写一个类似的@RoutingWith("slaveDataSource")注解,放到某个 Controller 的方法上,这个方法内部就自动选择了对应的资料源,代码看起来应该像这样:
@Controller
public class MyController {
@Get("/")
@RoutingWith("slaveDataSource")
public String index() {
return "html... www.liaoxuefeng.com";
}
}
这样,完全不修改应用程序的逻辑,只在必要的地方加上注解,自动实作动态资料源切换,这个方法是最简单的,
想要在应用程序中少写代码,我们就得多做一点底层作业:必须使用类似 Spring 实作宣告式事务的机制,即用 AOP 实作动态资料源切换,
实作这个功能也非常简单,撰写一个RoutingAspect,利用 AspectJ 实作一个Around拦截:
@Aspect
@Component
public class RoutingAspect {
@Around("@annotation(routingWith)")
public Object routingWithDataSource(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, RoutingWith routingWith) throws Throwable {
String key = routingWith.value();
try (RoutingDataSourceContext ctx = new RoutingDataSourceContext(key)) {
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
}
注意方法的第二个自变量RoutingWith是 Spring 传入的注解实体,我们根据注解的value()获取配置的 key,编译前需要添加一个 Maven 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
到此为止,我们就实作了用注解动态选择资料源的功能,最后一步重构是用字串常量替换散落在各处的"masterDataSource"和"slaveDataSource",
使用限制
受 Servlet 执行绪模型的局限,动态资料源不能在一个请求内设定后再修改,也就是@RoutingWith不能嵌套,此外,@RoutingWith和@Transactional混用时,要设定 AOP 的优先级,
本文代码需要 SpringBoot 支持,JDK 1.8 编译并打开-parameters编译自变量,
近期热文推荐:
1.1,000+ 道 Java面试题及答案整理(2021最新版)
2.劲爆!Java 协程要来了,,,
3.玩大了!Log4j 2.x 再爆雷,,,
4.Spring Boot 2.6 正式发布,一大波新特性,,
5.《Java开发手册(嵩山版)》最新发布,速速下载!
觉得不错,别忘了随手点赞+转发哦!













0 评论